What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is the abnormal cell growth in some areas of the skin. There are several types, including melanoma, although it is the lowest frequency is the most important, because it can be fatal.
Skin cancer is the most common worldwide, and has been a significant increase in recent years.
Who are more likely to cause skin cancer?
- Physical aspects: People who have blond hair or coppery color, white skin, freckles, blue eyes or light-colored.
- Climate / Geography: People living in sunny climates or who live in areas with decreased ozone layer.
- personal and family history / o: People with a history of skin cancer, especially melanoma, are people at higher risk.
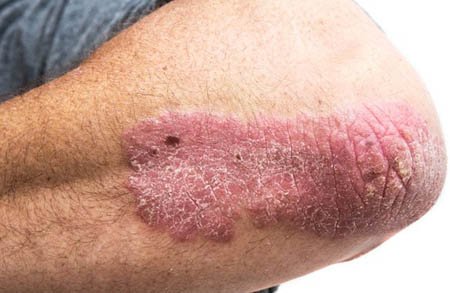
- Previous injuries: The presence of large number of moles (more than 50) or moles of atypical appearance (various colors, irregular shape), actinic keratoses (lesions rough or crusty appearance), scars in which a wound that does not heal appears.
Symptoms and signs: Symptoms and signs of skin cancer vary from person to person and between these can include:
- Skin changes, like a new mole or one that changes in size, shape or color.
- Spot, mole or ulcer with changes such as itching, tenderness and / or pain.
- small, smooth, shiny, pale or serous injury.
- Red Spot flat, rough, dry or scaly, crusted.
- A mole that is growing rapidly.
- A scaly or crusty skin growth.
- A wound that will not heal.
- A place on the skin that feels rough like sandpaper.
Many of these symptoms are not necessarily cancer, but if one or more of them is observed, for more than two weeks, consult your doctor.
Can you prevent skin cancer?
Although it can not completely prevent skin cancer, you can reduce their risk by protecting against ultraviolet radiation, detecting small changes in moles, which may be treated prior malignancy, and treatment of actinic keratosis ( rough skin lesions), which can be transformed into cancer.
Behaviors to reduce the risk of skin cancer
- Use sunscreen cream: Use a sunscreen or sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF by its initials in English) of at least factor 30, even on cloudy days. You must put on your skin the sunscreen 30 minutes before going out in the sun in all areas where the sun’s rays come directly, even in the ears and on the back the neck part. If bathing, great sweating or after 2 hours of direct sunlight permanence.
- Using wide-brimmed hats, protective clothing and sunglasses: A wide-brimmed hat will help protect from the sun: the face, neck and ears. A hat with a brim of 15.2 cm. around is the best. Use sunglasses to protect your eyes. Choose sunglasses that block ultraviolet-A (UVA) and ultraviolet-B (UVB) rays.
- Not seek to acquire a tan: salines not go tanning. Tanning booths damage your skin like you’re exposed to direct sunlight.
- Avoid the sun: The more you make the sun damage your skin, the greater the likelihood of premature wrinkles, skin cancer and other skin problems. The effect is cumulative. Avoid exposure to the sun between 10 and 16 hours.
What else should I do?
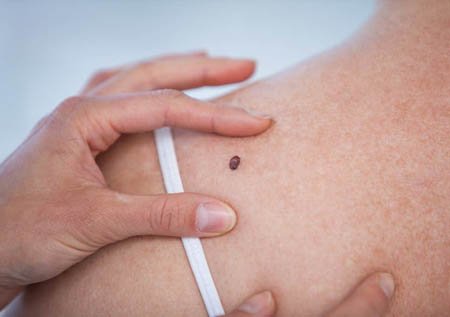
Lunar assessment: See if there have been changes in a mole or a new one has appeared. Any mole that appears after age 30 should be carefully reviewed and evaluated by a physician.
To easily remember the criteria for identifying suspicious lesions of cutaneous melanoma (malignant skin tumor), the ABCDE criteria were established:
- A by symmetry: A mole that imaginarily divided into two, is not equal on both sides.
- B Edge: a mole blurry or jagged edges.
- C for color: Changes in the color of a mole, including darkening, spread of color, loss of color or appearance of multiple colors such as blue, red, white, pink, purple or gray.
- D for diameter: A mole larger than 5 mm.
- E for elevation or evolution: a place that is raised above the skin and has a rough surface or grows rapidly.
Remember, skin cancer can be treated successfully if diagnosis is early.
Does skin cancer can be hereditary?
Yes, it’s important to watch your family if there is one or more relatives with melanoma.
